- Land
- Labor
- Capital
- Two Types
- Human Capital => when people acquire skills and knowledge through experience and education
- Physical Capital => can be anything like
- Money
- Tools
- Buildings
- Equipments
- Machinery
- Entrepreneurship
_________________________________________________________________________________
Key Vocabulary
- Trade Off
- An alternative that sacrifice when we make a decision
- Scarcity reads to trade off
- Opportunity Cost
- The most desirable alternative given up as a result of a decision
- A type of trade off
- Guns or Butter
- Trade off that the government makes when choosing between wether to produce more or less military or consumer goods
- Thinking at the Margins
- Deciding wether to add or subtract one additional units of some resource
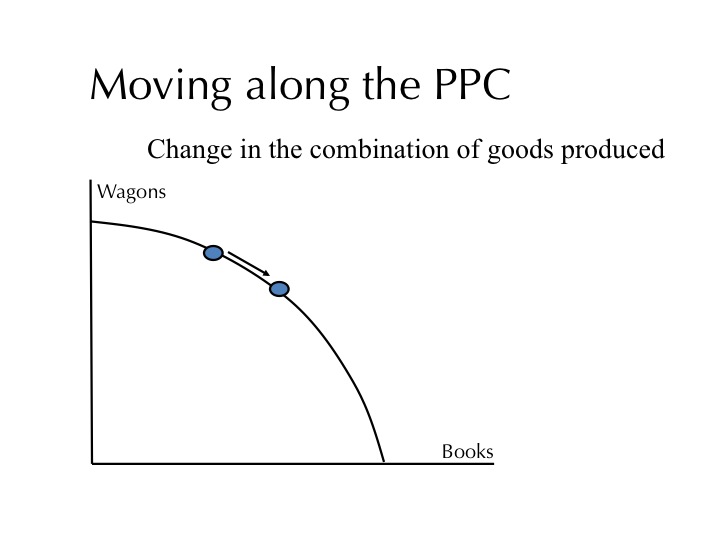
- Production Possibilities
- Graph (PPG)
- Curve (PPC)
- Frontier (PPF)
- Graphs that shows alternative ways to use an economics resources
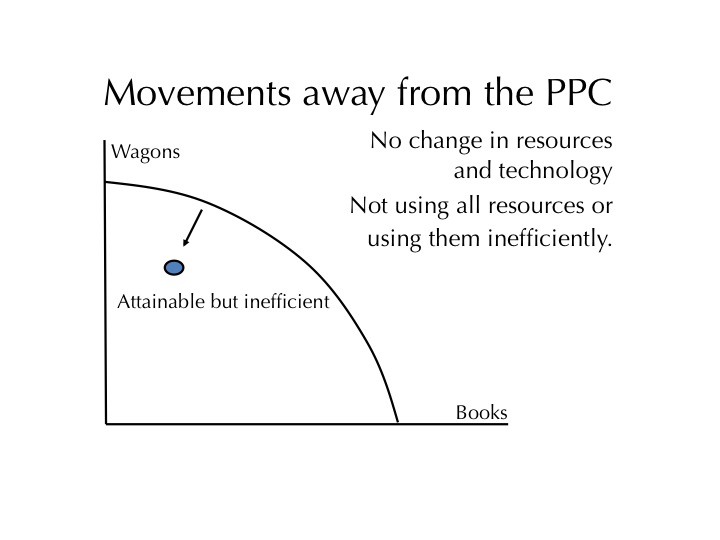
- Efficiency
- Using resources in such a way to maximize the production of goods and services
- Increases profit
- Underutilization
- Opposite of efficiency
- Using fewer resources then an economy is capable of using
- Leads to decrease in profits
_________________________________________________________________________________
Four Key Assumptions About PPG
- Only two goods can be produced
- Full Employment of resources
- Fixed Resources
- Fixed Technology